本文最后更新于:14 天前
pytorch实现线性回归
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2019/3/6 19:12
# @Author : Seven
# @File : LinearRegression.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# function : pytorch实现线性回归
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置超参数
input_size = 1
output_size = 1
num_epochs = 60
learning_rate = 0.001
# 初始化数据集
x_train = np.array([[3.3], [4.4], [5.5], [6.71], [6.93], [4.168],
[9.779], [6.182], [7.59], [2.167], [7.042],
[10.791], [5.313], [7.997], [3.1]], dtype=np.float32)
y_train = np.array([[1.7], [2.76], [2.09], [3.19], [1.694], [1.573],
[3.366], [2.596], [2.53], [1.221], [2.827],
[3.465], [1.65], [2.904], [1.3]], dtype=np.float32)
# 初始化线性模型
model = nn.Linear(input_size, output_size)
# 初始化损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 训练模型
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# Convert numpy arrays to torch tensors
inputs = torch.from_numpy(x_train)
targets = torch.from_numpy(y_train)
# Forward pass
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
# Backward and optimize
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
print('Epoch [{}/{}], Loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1, num_epochs, loss.item()))
# Plot the graph
predicted = model(torch.from_numpy(x_train)).detach().numpy()
plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'ro', label='Original data')
plt.plot(x_train, predicted, label='Fitted line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Save the model checkpoint
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'linear.ckpt')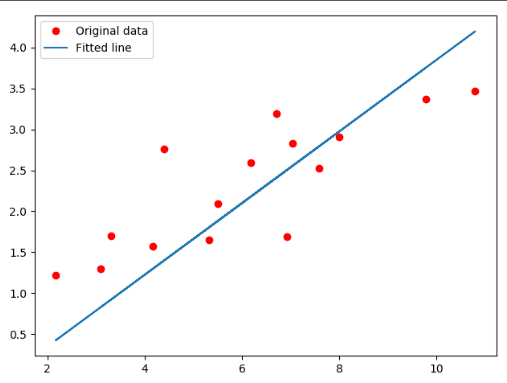
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!